Description
Oxygen Mask price in bd 2025
Introduction
Oxygen therapy is an essential medical intervention for individuals with respiratory conditions. Among the various oxygen delivery devices, the oxygen mask plays a crucial role in supplying higher concentrations of oxygen compared to nasal cannulas. This article explores the function, types, benefits, usage, maintenance, and potential complications of oxygen masks.
What is an Oxygen Mask price in bd 2025?
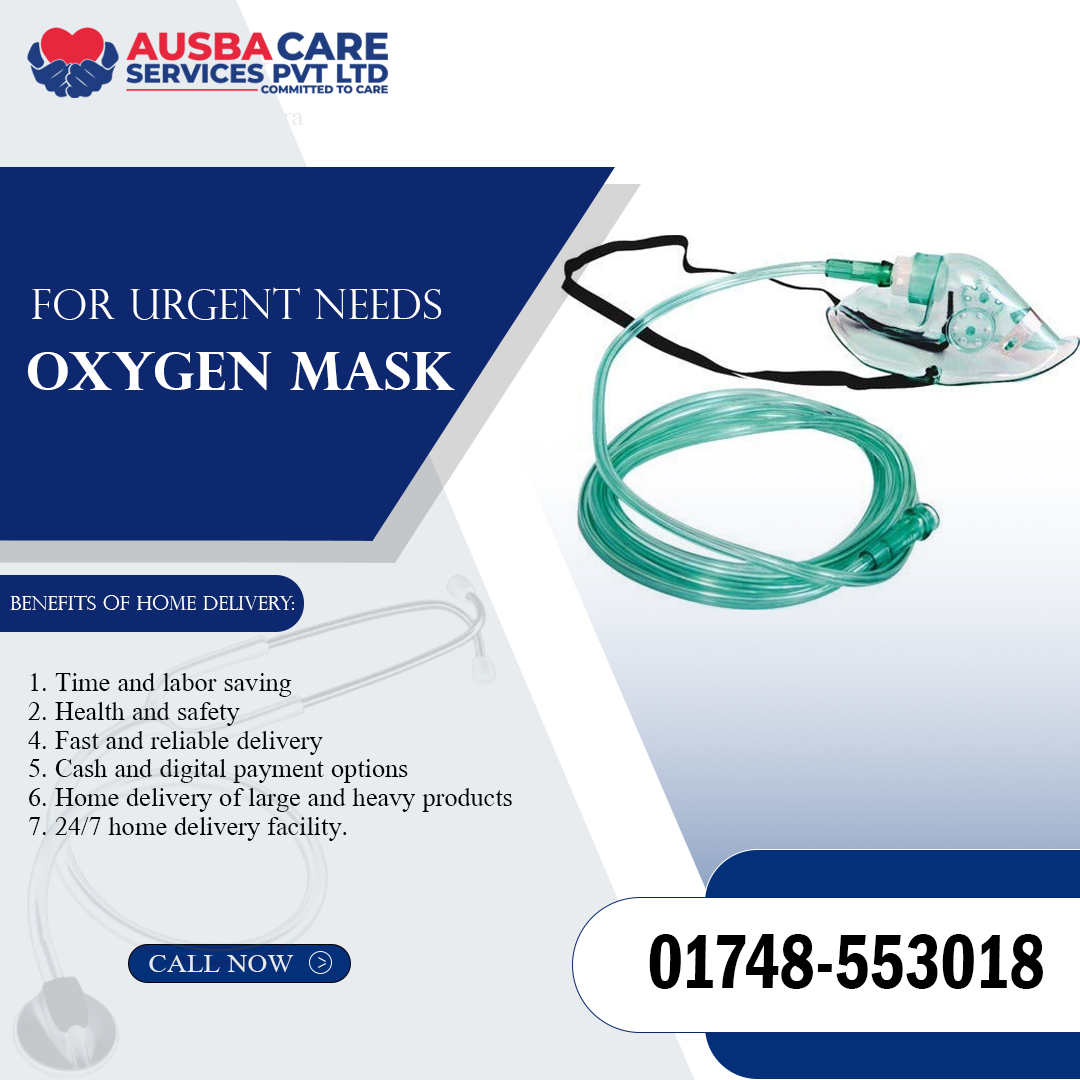
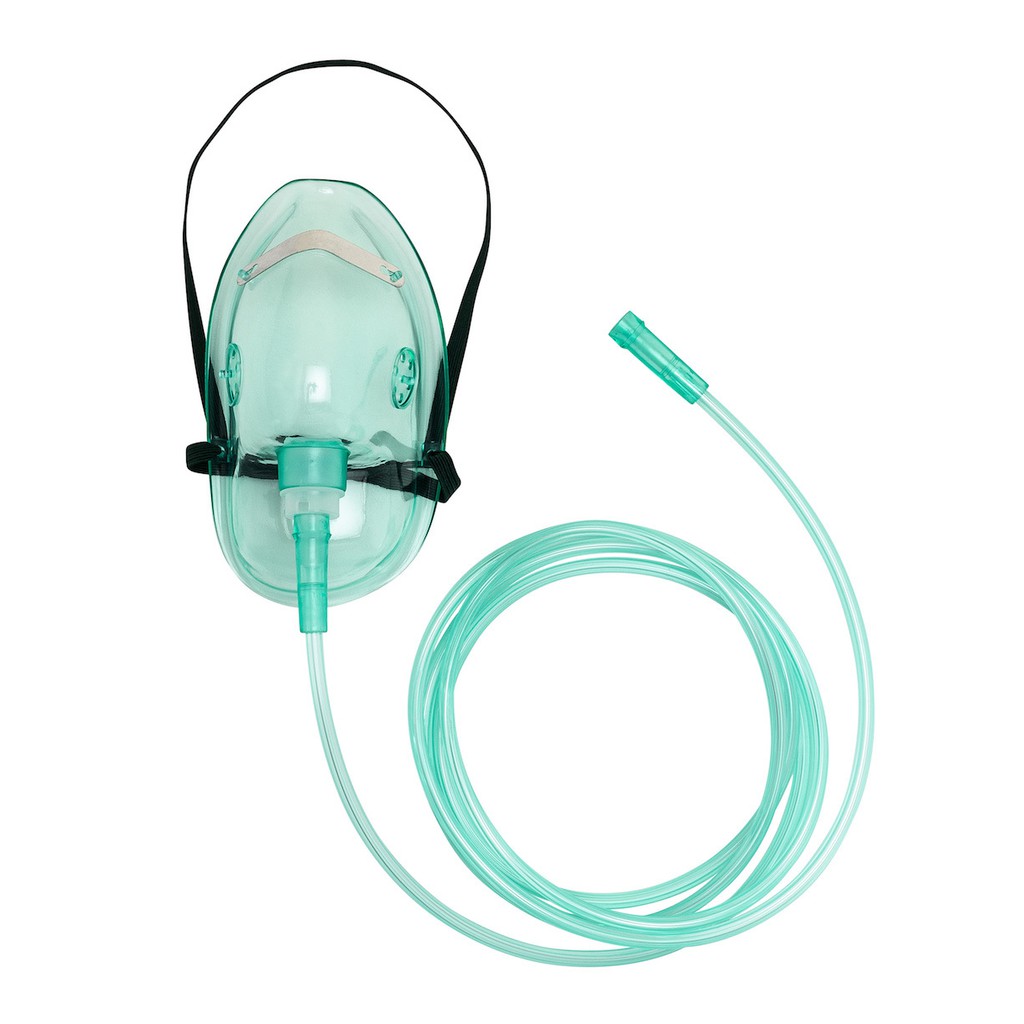
An oxygen mask is a medical device that covers the nose and mouth, allowing oxygen to be delivered from an external source, such as an oxygen cylinder or concentrator, directly to the patient’s airways. It is secured with elastic straps and is used in hospitals, emergency situations, and home care settings. Oxygen Mask
How Does an Oxygen Mask Work?
The oxygen mask is connected to an oxygen supply via tubing and a flow meter, which regulates the oxygen concentration and flow rate. The mask ensures that a controlled amount of oxygen reaches the patient while reducing the intake of surrounding air. Flow rates typically range from 5 to 15 liters per minute (LPM), depending on the mask type and patient needs.
Benefits of Using an Oxygen Mask
- Higher Oxygen Concentration – Delivers a more controlled and enriched oxygen supply than a nasal cannula.
- Suitable for Various Conditions – Used in hospitals, emergencies, and home therapy for moderate to severe respiratory conditions.
- Different Oxygen Delivery Options – Available in various designs to meet specific patient needs.
- Short-Term and Emergency Use – Effective for acute conditions where immediate oxygen therapy is required.
- Prevents Rebreathing of Carbon Dioxide – Certain mask designs minimize CO2 buildup, ensuring efficient oxygenation.
Types of Oxygen Masks
There are several types of oxygen masks designed for different medical situations:
- Simple Face Mask – Used for low-to-moderate oxygen needs, typically delivering 5-10 LPM of oxygen.
- Venturi Mask – Provides precise oxygen concentration by mixing oxygen with ambient air, ideal for patients requiring controlled oxygen therapy.
- Non-Rebreather Mask (NRB) – Equipped with a one-way valve and reservoir bag to deliver high-concentration oxygen (10-15 LPM), commonly used in emergencies.
- Partial Rebreather Mask – Similar to an NRB but allows some exhaled air to mix with Oxygen Mask oxygen, providing moderate oxygen concentration.
- Reservoir Mask – Stores extra oxygen for inhalation, conserving oxygen supply and improving efficiency.
- Pediatric Oxygen Masks – Designed for children and infants, ensuring a proper fit and effective oxygen delivery.
Who Needs an Oxygen Mask price in bd 2025?
Oxygen masks are prescribed for individuals with conditions that significantly reduce blood oxygen levels, including:
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- Asthma Attacks
- Pneumonia
- Heart Failure
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
- Post-Surgical Recovery
- Severe COVID-19 Cases
- Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
How to Use an Oxygen Mask
- Prepare the Equipment – Connect the mask to the oxygen supply and set the prescribed flow rate.
- Position the Mask – Place the mask over the patient’s nose and mouth, ensuring a snug fit.
- Secure the Straps – Adjust the elastic straps around the head for a comfortable yet firm hold.
- Breathe Normally – The patient should inhale and exhale naturally while receiving oxygen.
- Monitor Oxygen Levels – Use a pulse oximeter to check oxygen saturation and ensure optimal therapy.
Care and Maintenance of an Oxygen Mask
To maintain hygiene and efficiency, proper care is essential:
- Daily Cleaning – Wash the mask with mild soap and water, then air dry.
- Regular Disinfection – Soak in a medical disinfectant solution at least once a week.
- Replace When Necessary – Change the mask every one to two weeks or as recommended by healthcare providers.
- Check for Damage – Inspect for cracks, leaks, or loose connections to prevent oxygen loss.
Potential Complications and How to Prevent Them
While oxygen masks are generally safe, some issues may arise:
- Skin Irritation or Pressure Sores – Adjust the straps to prevent excessive pressure on the face.
- Dryness and Mucosal Irritation – Use a humidifier to add moisture to the oxygen supply.
- Oxygen Toxicity – Prolonged exposure to high oxygen levels can cause lung damage; adhere to prescribed flow rates.
- CO2 Retention – Ensure proper mask ventilation to prevent CO2 buildup.
- Fire Hazard – Keep oxygen sources away from flames, smoking, and heat sources.
Alternatives to Oxygen Masks
Other oxygen delivery systems may be used based on the patient’s oxygen needs:
- Nasal Cannula – Suitable for low-flow oxygen therapy (1-6 LPM) and long-term use.
- High-Flow Nasal Cannula (HFNC) – Provides humidified oxygen at higher flow rates.
- CPAP/BiPAP Machines – Used for patients with sleep apnea or severe respiratory distress.
- Tracheostomy Masks – Designed for patients with tracheostomies requiring oxygen support.
Conclusion
Oxygen masks are a vital tool in respiratory therapy, providing essential oxygen support for patients with various medical conditions. Their ability to deliver controlled oxygen concentrations makes them indispensable in hospitals, emergency care, and home therapy. Proper usage, maintenance, and adherence to medical guidelines ensure safe and effective oxygen delivery while minimizing potential complications. Whether in routine therapy or critical care settings, oxygen masks remain a cornerstone of modern respiratory treatment.






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.